Feature Image: Digging a compost pit
nytimes.com
The organic matter formed through degradation of decomposable biomass and which is rich in nutrients for the growth and development of plants is called as compost. Compost is the organic matter which is saturated with nutrients. It is used in gardens, land scaping, horticulture, and agriculture.
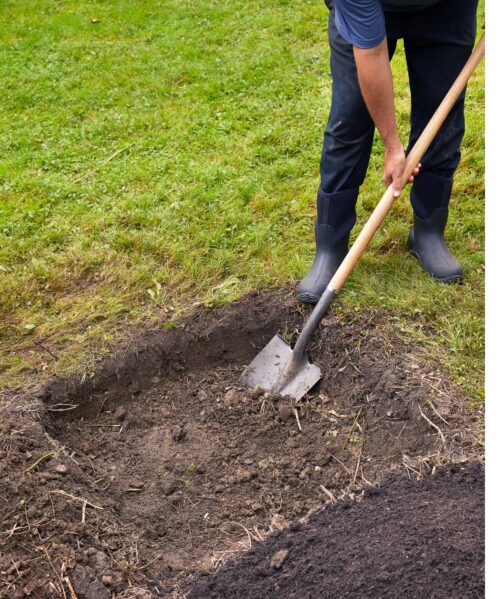
The process of composting simply requires making a heap of wetted organic matter known as green waste (leaves, food waste) and waiting for the materials to break down into humus after a period of weeks or months. Traditionally, a pit of specified measurement is dug out and plastered from inside. It is in this pit that biodegradable matter is deposited.
The biodegradable matter may be composed of leaves of plants, agricultural waste, kitchen waste, food leftovers, etc. These matters are mixed with cow dung, straw, and crop stables wetted with animal urine in the cattle sheds. The compost pit is covered with fine soil when it is filled completely. The pit is watered from time to time.
Within some days biodegrading of matter filled inside the pit starts. A number of worms, bacteria and fungi join their duties of decomposing the biomass in the compost pit. In the middle section of the pit a high temperature is produced which is sufficient to kill the seeds of grasses and even worms.
However, some worms are efficient enough to tolerate that much of temperature. When the process of decomposition gets completed, the compost or the bi-manure is prepared. It is dug out of the pit put into sacs and shifted to the crop fields where it is scattered in the field.
The bio-compost is beneficial to soil. It maintains the soil structure, increases its porosity, and water holding capacity. Like synthetic fertilizers, it does not damage the soil structure, and also does not alter its pH.
Modern composting technique is a multi-step, closely monitored process with measured inputs of water, air, and carbon- and nitrogen-rich materials.
The decomposition process during composting is aided by shredding the plant matter, adding water and ensuring proper aeration by regularly turning the mixture.
A number of Worms and fungi further break up the material. Aerobic bacteria and fungi manage the chemical process by converting the inputs into heat, carbon dioxide and ammonium. The nitrogen is the form of ammonium (NH4) used by plants. When available ammonium is not used by plants it is further converted by bacteria into nitrates (NO3) through the process of nitrification.
The compost itself is beneficial for the land in many ways. It acts as a soil conditioner and a fertilizer. It improves the soil quality by addition of vital humus or humic acids, which also acts as a natural pesticide for soil.
In ecosystems, compost is useful for erosion control, land and stream reclamation, wetland construction, and as landfill cover.
Organic ingredients intended for composting can alternatively be used to generate biogas through anaerobic digestion.
Key Words : Making compost, better health of soil, synthetic fertilizers,