1. Trait-A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and trait-B in 60%of the same population. Which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Ans. Trait-A
2. How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Ans. Through experiment of Mendel we come to know that if plants with two mutually different characters are crossed together, only one character appears in the first generation. The second character remains hidden. Thus the character which appeared in the first generation is a dominant character. When plants of first generation were self-pollinated the recessive character of the first generation appeared in the second generation. Thus it is proved that characters may be dominant and recessive.
3. How does creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Ans. Variations help different individuals in many different ways. For example some bacteria can survive in extreme temperature and can survive in very hot conditions. On the other hand some bacteria cannot survive in very hot conditions. So, when there is extreme temperature only first type of bacteria can survive. Others are sure to die off. In this way variations promote survival.
4. How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Ans. Mendel crossed long pea plants with round seeds and dwarf pea plants with wrinkled seeds and found that
(i) All the plants in F1 generation were long and had round seeds. This shows that characters of length and round shape of seeds are dominant characters.
(ii) In F2generation some plants show new combination- like long with wrinkled seeds; and dwarf with round seeds.
From (i) and (2) it can be concluded that characters of length, shapes of seeds like round and wrinkled, colours of seeds like yellow and green all are independent. These characters are inherited freely.
5. A man with Blood Group A marries a woman with Blood Group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits Blood Group A or Blood Group O is dominant? Why or Why not?
Ans. No, this information is not sufficient because the gene combination of man with blood group A
is not known. His gene combination may be any one out of IAIA or IAIO which is not clear. Thus gene combination or genotype must be known for determining blood group.
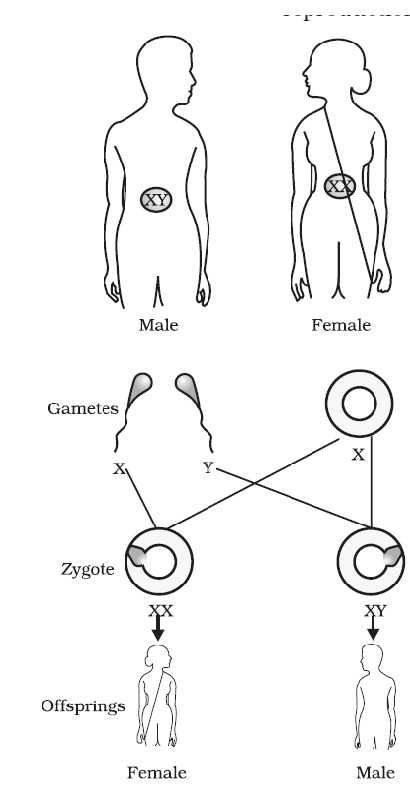
6. What is Sex-determination? How is the sex of a child determined in human being?
Ans. Determining male or female form of living organism through sexual reproduction is called as sex determination. Sex determination on a large scale is of two types- environmental, genetic and chromosome based.
When cells of human testis divide to form sperms then the pair of sex chromosome segregates into X and Y. Half the sperms get X chromosomes and the remaining half get Y chromosomes. The ova in females contain half the number of chromosomes than the normal cells like man. Egg cells produce ova but all the ova have only X chromosomes.
During fertilization it depends only on chance whether the X chromosome will fertilize the ovum or Y chromosome. If X-chromosome fertilizes the ovum the sex of the child will be XX or female but if Y chromosome fertilizes the ovum the sex of the child will be male or the XY.
Refer feature image by NCERT